0、题目列表
题目1、链表反转
题目2、链表是否有环
题目3、链表是否有环,并返回环的节点
题目4、合并两个有序链表
题目5、两个链表的第一个公共结点
题目6、链表中环的入口结点
题目7、链表中倒数最后k个结点
题目8、复杂链表的复制
题目9、删除链表的节点
题目10、删除链表中重复的结点
题目11、从尾到头打印链表
一、定义
1.定义
链表中每个节点有两部分组成,一是节点的value值,二是下一个节点在内存的地址。
2.指针
python中没有指针概念,类似指针的功能都是通过引用来实现的,代码中通过引用来建立结点之间的关系。
3.注意点
要注意的几个地方:
- 1.链表默认指向的是头节点,我们用while pHead:循环的时候需要用 pHead = pHead.next,否则一直在头节点循环,对pHead = pHead.next的理解为:pHead变量原本指向的是a节点的引用(内存地址),现在改为了指向下一个节点b,但是a节点没有消失还是在链表中,只是变量不在指向了
- 2.一般用cur变量(指针)指向当前节点,cur指向的只是当前链表中的一个节点的引用(或者说地址)
- 3.
4.基本操作
参考:https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1568825
class LNode(object):
#结点初始化函数, p 即模拟所存放的下一个结点的地址
#为了方便传参, 设置 p 的默认值为 0
def __init__(self, data, p=0):
self.data = data
self.next = p
class LinkList(object):
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
#链表初始化函数, 方法类似于尾插
def initList(self, data):
#创建头结点
self.head = LNode(data[0])
p = self.head
#逐个为 data 内的数据创建结点, 建立链表
for i in data[1:]:
node = LNode(i)
p.next = node
p = p.next
#链表判空
def isEmpty(self):
if self.head.next == 0:
print "Empty List!"
return 1
else:
return 0
#取链表长度
def getLength(self):
if self.isEmpty():
exit(0)
p = self.head
len = 0
while p:
len += 1
p = p.next
return len
二、题目
题目1、链表反转
1.整体思路
需要定义个外部新链表存储新生成的链表,while里面有四步操作:
定义两个指针,pre前一个节点指针, cur当前指针
首先外部定义个pre = None来承接新的链表
1.定义tmp = pHead.next,将当前节点之后的节点先存起来
2.将当前节点反转,指向外部定义pre变量:pHead.next = pre
3.更新外部pre,让pre存储最新节点:pre = pHead
4.当前节点已经反转完毕,开始下一个节点:pHead = pHead.next
2.具体算法
反转链表:输入一个链表,反转链表后,输出新链表的表头。
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.next = None
class Solution:
# 返回ListNode
class Solution:
def ReverseList(self , head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
# write code here
if not head or not head.next:
return head
pre = None #前指针
cur = head #当前指针
while cur: #循环当前指针
tmp = cur.next #先把后指针咱存
cur.next = pre #把当前指针指向前指针
pre = cur #前指针后移
cur = tmp #当前指针后移
return pre #返回前指针,反转后前指针是头结点
题目2、链表是否有环
1.整体思路
有两种思路:
2.具体算法
(1)方法一:剑指offer:55题
题目:链表中环的入口结点----给一个链表,若其中包含环,请找出该链表的环的入口结点,否则,输出null。
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.next = None
class Solution:
def EntryNodeOfLoop(self, pHead):
# write code here
node = []
if not pHead:
return None
while pHead:
if pHead in node:
return pHead
else:
node.append(pHead)
pHead = pHead.next
方法二:
nowcoder 在线编程:top5
题目:链表中环的入口结点----给一个链表,若其中包含环,请找出该链表的环的入口结点,否则,输出null。你能给出空间复杂度O(1)的解法么
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.next = None
class Solution:
def hasCycle(self , head ):
# write code here
p = head
q = head
while(p!=None and p.next!=None):
p = p.next.next
q = q.next
if p == q:
return True
return False
题目3、链表是否有环,并返回环的节点
1.整体思路
2.代码
class Solution:
def detectCycle(self , head ):
# write code here
if head is None or head.next is None:
return None
f = head
s = head
while(s!=None and f.next!=None):
f = f.next.next
s = s.next
if s is None or f is None:
return None
if s == f: ####找到指针相交点,但是不一定是入口节点
s = head #### 让慢指针从新从开始节点走,快慢节点相交的位置,就是入口节点
while s is not f:
s = s.next
f = f.next
return s
return None
题目4、合并两个有序链表
来源:剑指offer第25题
1.整体思路
(1)因为两个链表都是有序的,所以每次只需要比较两个链表头结点大小就行了
(2)较小的值需要三步操作:a.把当前节点(指针)赋给新头结点的next b.当前节点指针下移动 c.新节点指针下移
(3)对最终剩余的链表处理,直接拼接赋值即可
2.代码
# 写法1
class Solution:
# 返回合并后列表
def Merge(self, pHead1, pHead2):
# write code here
p = pHead = ListNode(0)
while pHead1 and pHead2:
if pHead1.val<pHead2.val:
pHead.next = pHead1
pHead1 = pHead1.next
pHead = pHead.next
else:
pHead.next = pHead2
pHead2 = pHead2.next
pHead = pHead.next
if pHead1:
pHead.next = pHead1
if pHead2:
pHead.next = pHead2
return p.next
# 写法2:
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.next = None
class Solution:
def Merge(self , pHead1: ListNode, pHead2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
# write code here
head = p = ListNode(0)
while pHead1 and pHead2:
if pHead1.val<pHead2.val:
p.next = pHead1
pHead1 = pHead1.next
else:
p.next = pHead2
pHead2 = pHead2.next
p = p.next
p.next = pHead1 or pHead2
return head.next
题目5、两个链表的第一个公共结点
来源:剑指offer第52题
1.整体思路
本题有两种解题思路:
- 第一种:
时间复杂度:o(n+m)空间复杂度:o(n)
(1)设置一个set()存储其中一个链表,循环第二个链表
- 第二种:
时间复杂度:o(n+m)空间复杂度:o(1)
核心思想就是:两个链表拼接后(分别拼接),开始循环,肯定同时到达有共同节点的位置
例如:链表:
1->2->3->4->5;
0->8->4->5
两个链表分别拼接后组成:
1->2->3->4->5->0->8->4->5;
0->8->4->5->1->2->3->4->5;
那么在最后4的位置首次相遇
(1)创建两个指针A和B分别指向两链表的初始节点,然后让指针A遍历链表1的所有节点;同理指针B也遍历链表2的所有节点;
(2)当指针A和指针B都遍历完各自的节点后,开始互换赛道,让指针A去走链表2;而指针B则走链表1;
(3)依然是遍历,但是这次两指针就会在某一个点相遇!这个相遇点就是我们要找的第一个公共节点。
2.代码
#第一种算法:
class Solution:
def FindFirstCommonNode(self , pHead1 , pHead2 ):
# write code here
s1 = set()
while pHead1:
s1.add(pHead1)
pHead1 = pHead1.next
while pHead2:
if pHead2 in s1:
return pHead2
pHead2 = pHead2.next
return None
#第二种:
class Solution:
def FindFirstCommonNode(self , pHead1 , pHead2 ):
# write code here
p1, p2 = pHead1, pHead2
while p1!=p2:
p1 = p1.next if p1 else pHead2
p2 = p2.next if p2 else pHead1
return p1
题目6、链表中环的入口结点
来源:剑指offer第23题
给一个长度为n链表,若其中包含环,请找出该链表的环的入口结点,否则,返回null。
1.整体思路
本题有两种解题思路:
第一种:
(1)设置一个set()存储其中一个链表,循环链表
第二种:
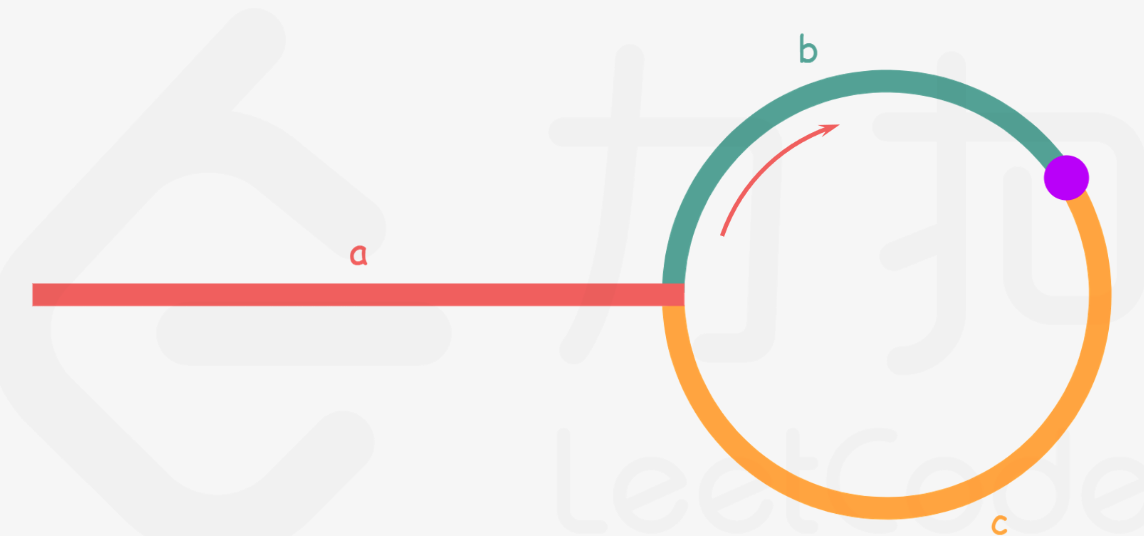
通过双指针,一个快纸质,一个慢指针,快指针比慢指针每次多走一步,如果能相遇则证明有环,如何找环的入口节点,可以证明 a=c+i(b+c) i为整数。
(1)定义一个快指针fast,一个慢指针slow
(2)开启一个死循环,让快指针每次比慢指针多走一步
(3)找到相遇节点,让快指针从头开始走,慢指针继续走,再次相遇就是入口节点
为什么再次相遇就是入口节点呢?证明:
fast = a+b+i(b+c) #i是整数
slow = a+b
fast = 2slow
=>a+b+i(b+c) = 2(a+b)
=>i(b+c) = a+b
=>a = i(b+c) -b
=> a = (i-1)(b+c)+c
也就是说a的长度等于c+整数的还
思路参考:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-lcci/solution/huan-lu-jian-ce-by-leetcode-solution-s2la/
2.代码
#第一种算法:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def EntryNodeOfLoop(self, pHead):
# write code here
s1 = set()
while pHead:
if pHead in s1:
return pHead
else:
s1.add(pHead)
pHead = pHead.next
return None
#方法二:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def EntryNodeOfLoop(self, pHead):
# write code here
slow = fast = pHead
while 1:
if not fast or not fast.next:
return None
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
if slow == fast:
break
fast = pHead
while fast!=slow:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
return fast
题目7、链表中倒数最后k个结点
来源:剑指offer第22题
输入一个长度为 n 的链表,设链表中的元素的值为 ai ,返回该链表中倒数第k个节点。
如果该链表长度小于k,请返回一个长度为 0 的链表。
1.整体思路
本题有两种解题思路:
第一种:
(1)设置一个list存储其中一个链表,循环链表,取倒数第k个
第二种:
(1)设置两个指针,一个快指针,一个慢指针,快指针先走k步,然后两个指针在一起走,
#第一种方法:
class Solution:
def FindKthToTail(self , pHead: ListNode, k: int) -> ListNode:
# write code here
nodelist = []
while pHead:
nodelist.append(pHead)
pHead = pHead.next
if k>len(nodelist) or k==0:
return None
return nodelist[-k]
#第二种方法:
class Solution:
def FindKthToTail(self , pHead: ListNode, k: int) -> ListNode:
# write code here
fast = slow = pHead
for i in range(k):
if not fast or not fast.next:
return None
fast = fast.next
while fast:
fast = fast.next
slow = slow.next
return slow
题目8、复杂链表的复制
来源:剑指offer第35题
1.整体思路
使用递归的方式最简单
2.代码
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class RandomListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.label = x
# self.next = None
# self.random = None
class Solution:
# 返回 RandomListNode
def Clone(self, pHead):
# write code here
if not pHead:
return None
p = RandomListNode(pHead.label)
p.random = pHead.random
p.next = self.Clone(pHead.next)
return p
题目9、删除链表的节点
来源:剑指offer第18题
1.整体思路
有两种方法:
第一种:使用一个指针:cur ,当找到要删除的节点,用后面节点的值替换掉当前节点的值,但是对于这种方式对最后一个节点无法处理({1,2,4,5},5如果要删除5节点)(但是牛客网通过了)
第二种:使用双指针,找到要删除的节点后,把后一个节点赋给前一个节点
2.代码
第一种:
class Solution:
def deleteNode(self , head: ListNode, val: int) -> ListNode:
# write code here
if not head:
return None
if head.val == val:
return head.next
cur = head
while cur:
if cur.val == val:
cur.val =cur.next.val
cur.next = cur.next.next
else:
cur = cur.next
return head
第二种:
class Solution:
def deleteNode(self , head: ListNode, val: int) -> ListNode:
# write code here
if not head:
return None
if head.val == val:
return head.next
pre = head
cur = head.next
while cur:
if cur.val == val:
pre.next =cur.next
cur = cur.next
else:
pre = pre.next
cur = cur.next
return head
题目10、删除链表中重复的结点
来源:剑指offer第76题
题目:在一个排序的链表中,存在重复的结点,请删除该链表中重复的结点,重复的结点不保留,返回链表头指针。 例如,链表 1->2->3->3->4->4->5 处理后为 1->2->5
1.整体思路
第一种方法:比较简单,但是空间复杂度O(n)时间复杂度O(n)
设置两个list,一个存储要删除的节点,一个存储要保留的节点,最后在重建链表
第二种方法:设置两个指针,空间复杂度O(1)时间复杂度O(n),当前节点需要有序
(1)设置一个新增头节点top,设置一个前指针pre,一个当前指针cur,一个tmp用来记录当前删除节点的值(主要是为了后面的节点和删除的节点对比,判断新节点是否需要删除),
第一种:
class Solution:
def deleteDuplication(self , head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
# write code here
save = []
de = []
if not head:
return None
while head:
if head.val not in de:
if head.val in save:
de.append(head.val)
save.remove(head.val)
else:
save.append(head.val)
head = head.next
if not save:
return None
star = cur = ListNode(save[0])
for i in save[1:]:
cur.next = ListNode(i)
cur = cur.next
return star
第二种:
class Solution:
def deleteDuplication(self , head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
# write code here
if not head or not head.next:
return head
pre = top = ListNode(0)
pre.next = cur =head
tmp = ''
while cur:
if(cur.next and cur.val == cur.next.val ) or (tmp==cur.val):
pre.next = cur.next
tmp = cur.val
else:
pre = pre.next
cur = cur.next
return top.next
题目11、从尾到头打印链表
来源:剑指offer第1题
题目:输入一个链表的头节点,按链表从尾到头的顺序返回每个节点的值(用数组返回)。
1.整体思路
2.代码
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
#
class Solution:
def printListFromTailToHead(self , listNode) :
result = []
while(listNode):
result.append(listNode.val)
listNode = listNode.next
return result[::-1]
